Artificial Olfaction
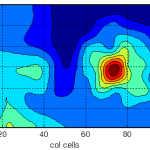
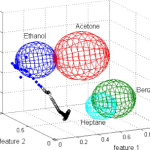
Artificial olfaction involves the use of gas-sensing technology and intelligent algorithms to detect, identify, or localize volatile compounds in the air. This includes areas of general interest such as air quality evaluation, or more specific applications such as the detection and localization of toxic or greenhouse gas emissions such as methane, CO2, or sulfide derivatives. This “ability” is increasingly being integrated into mobile robots to both enhance their ability to interact with and understand their environment by detecting and processing gaseous substances, as well as to enhance the intelligent automation of monitoring processes that require the detection of volatile substances.
Artificial olfaction has a wide range of applications across multiple sectors. Our group focuses on the integration of this challenging and promising research topic with intelligent mobile robots, giving rise to applications like Environmental Monitoring, for detecting and tracking pollutants, harmful gases, and chemical leaks to ensure air quality and public safety, or Security, identifying and localizing hazardous substances for security purposes (like natural gas leaks within a house).
Numerous problems are caused by uncontrolled or illicit emissions of polluting gases that contribute to global warming or even cause direct harm to human health. Due to the abundance of pollution’s sources, many governments around the world have recently invested in implementing systems for the measurement and control of such emissions, including mobile robotic agents.
Research Areas:
Mobile olfactory robots can be used in several and relevant application areas where a better understanding of gas distribution is needed. Concretely, our research focuses on four main areas around this topic:
Related Projects:
- HOUNDBOT: Gas Mapping and Source Localisation with a Mobile Robot
 (Oct’21–Sep’23)
(Oct’21–Sep’23)
Regional Project - Robotic Gas Localization System for the FOXIRIS Team Within the ARGOS Challenge
 (Apr’15–Apr’17)
(Apr’15–Apr’17)
Tech. Transfer Project - IRO: Improvement of the sensorial and autonomous capability of Robots through Olfaction
 (Jan’14–Feb’19)
(Jan’14–Feb’19)
Regional Project - Development of a Mobile Robot with Olfactory Capability
 (Jan’09–Mar’14)
(Jan’09–Mar’14)
Regional Project