Jesús Moncada Ramírez
Professional profile
I hold a Bachelor’s Degree in Computer Engineering (Ingeniería Informática) and a Master’s Degree in Mechatronics Engineering (Ingeniería Mecatrónica) from the University of Málaga, and I currently work as a Research Engineer in the Machine Perception and Intelligent Robotics (MAPIR) group. My research focuses on developing advanced Computer Vision and Artificial Intelligence techniques to enhance the cognitive abilities of mobile robots.
In addition to my research work, I am actively involved in software development, with a particular interest in web programming and applying AI systems to optimize business processes. I have experience in designing microservice-based architectures, implementing authentication and authorization mechanisms, and integrating AI solutions into web platforms to improve their performance and scalability.
I enriched my academic background with an Erasmus exchange at the University of Padua (Italy), where I deepened my knowledge of advanced computing and AI. I am passionate about solving complex problems, exploring new technologies, and collaborating in multidisciplinary, international environments. In addition, I am fluent in Spanish, English, and Italian.
Conference papers
Modelos a gran escala para mapeo semántico en robótica móvil
Jornadas de Automática (JJAA) 2024 — Málaga, Spain
At the Jornadas de Automática 2024, organized by Comité Español de Automática (CEA) and held in Málaga, I had the honor of presenting the paper “Modelos a gran escala para mapeo semántico en robótica móvil” (“Large models for semantic mapping in mobile robotics”), co-authored with José-Raúl Ruiz-Sarmiento, José-Luis Matez-Bandera, and Javier González-Jiménez.
In this work, we proposed a method based on ConceptGraphs that leverages Large Language and Vision Models (LLMs and LVLMs) to build open-vocabulary semantic maps, incorporating two key improvements: adaptation to state-of-the-art LLMs such as Gemini 1.5 and ChatGPT-4o, and a refinement stage using the Reflection agentic workflow, which enables the model to self-evaluate and correct its own responses.
We validated the proposal through experiments in real-world environments from the ScanNet dataset, demonstrating its effectiveness in reducing errors and increasing the robustness of semantic mapping.


MAPIR members at the social dinner during the 2025 RBVM. 
MAPIR members during the 2025 RBVM main conference.
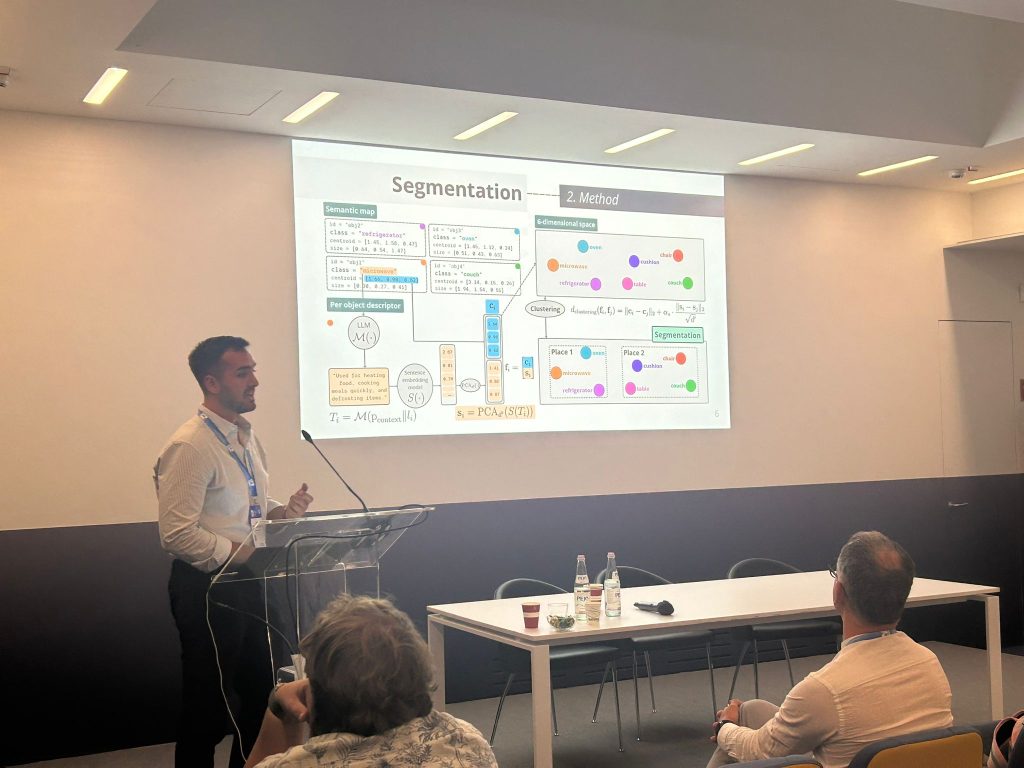
Segmentación semántica de instancias de objetos empleando un vocabulario abierto
Simposio CEA de Robótica, Bioingeniería, Visión Artificial y Automática Marina (RBVM) 2025 — Almería, Spain
The Simposio CEA de Robótica, Bioingeniería, Visión Artificial y Automática Marina 2025, held in Almería, Spain, featured our paper “Segmentación semántica de instancias de objetos empleando un vocabulario abierto” (“Semantic segmentation of object instances using an open vocabulary”), presented by my colleague Macorís Decena, with me as second author, together with José-Raúl Ruiz-Sarmiento and Javier González-Jiménez.
The work introduces TALOS, a modular method for open-vocabulary instance semantic segmentation. TALOS combines three stages—Tagging, Location, and Segmentation—to accurately detect and segment objects beyond the fixed categories of traditional datasets like COCO.
Qualitative evaluations demonstrated that TALOS offers richer semantic labels and more precise masks than standard closed-vocabulary tools, such as Detectron2, even in complex scenes.
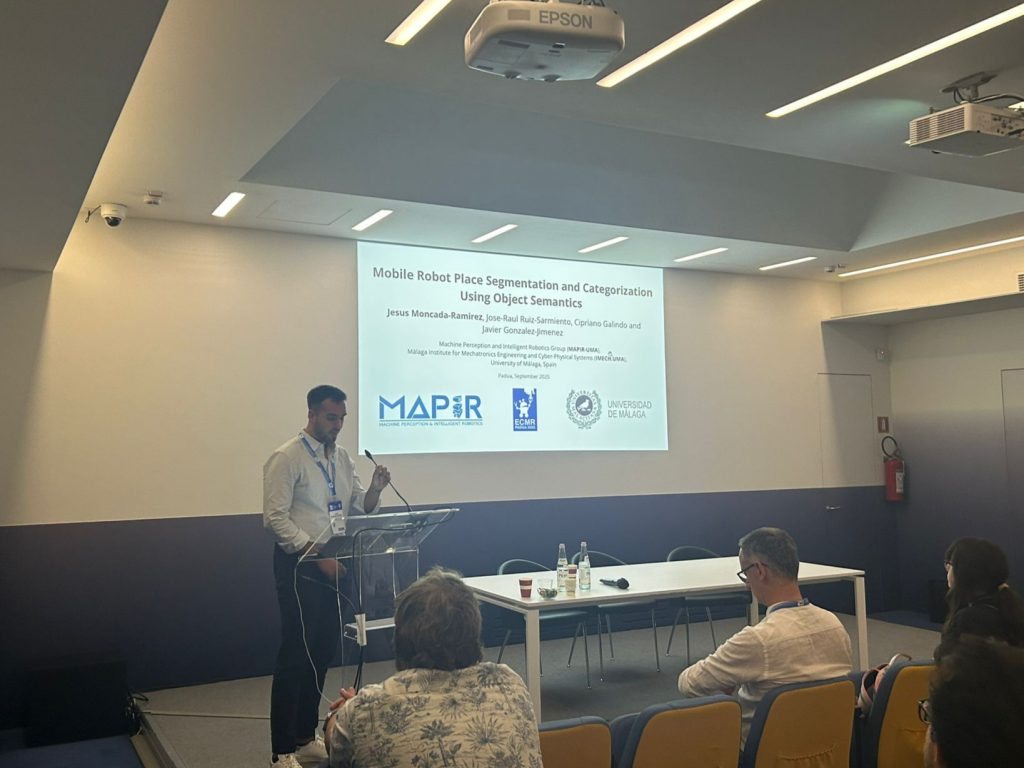
Mobile Robot Place Segmentation and Categorization Using Object Semantics
European Conference on Mobile Robots 2025 — Padua, Italy
The European Conference on Mobile Robots (ECMR) 2025, held in Padua, Italy, brought together researchers and professionals from robotics and artificial intelligence to share new ideas and technologies for autonomous mobile robots. At this event, I presented the paper “Mobile Robot Place Segmentation and Categorization Using Object Semantics”, coauthored with José-Raúl Ruiz-Sarmiento, Cipriano Galindo, and Javier González-Jiménez.
The paper proposes a method to segment and categorize indoor spaces by clustering objects based on their geometric properties and rich semantic information generated by LLMs and word/sentence embedding models, enabling more flexible and meaningful representations of environments.
Experiments on the ScanNet and SceneNN datasets demonstrate that this approach improves segmentation accuracy and provides more informative, open-set place descriptions compared with traditional room-based techniques.

Journal articles
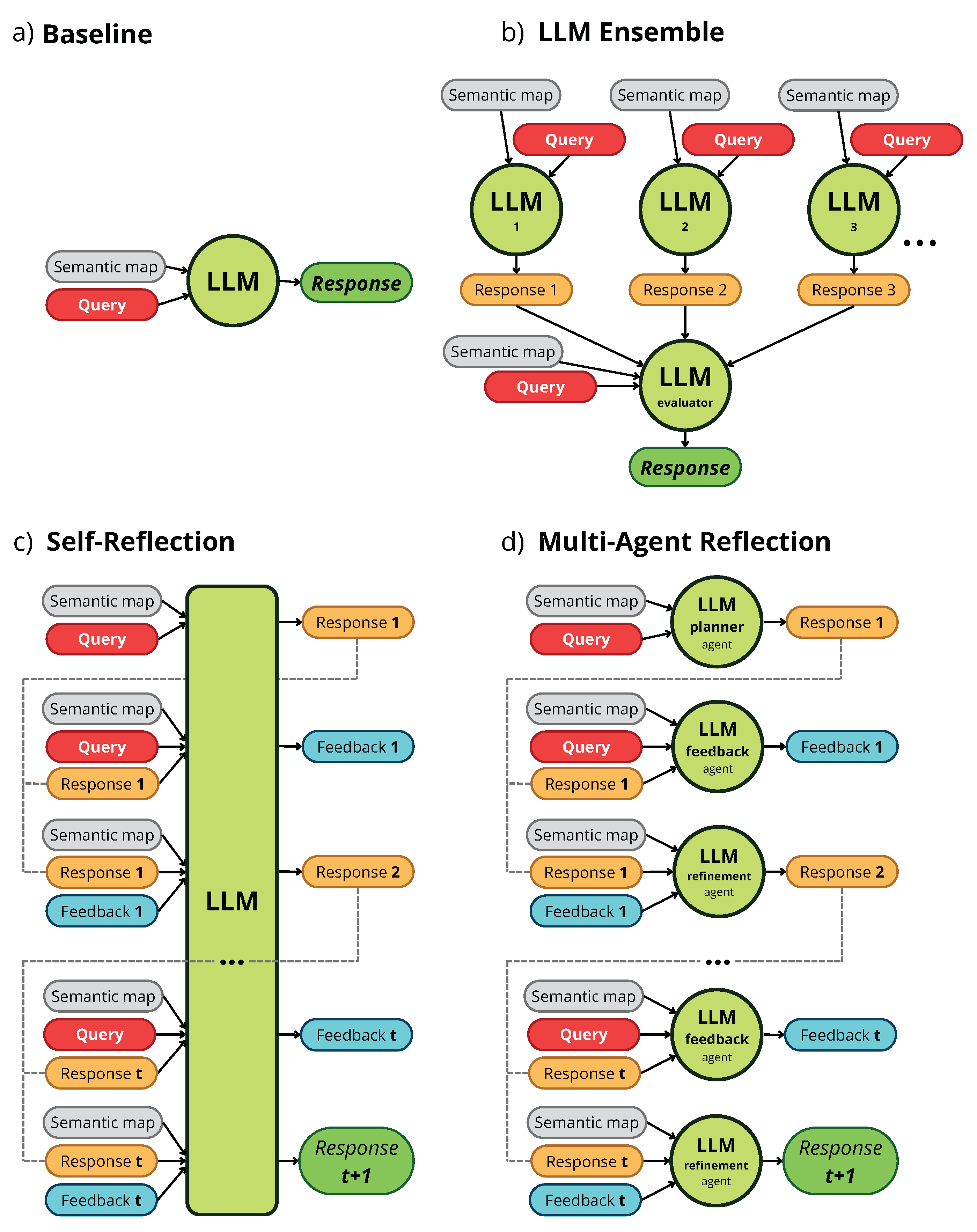
Agentic Workflows for Improving Large Language Model Reasoning in Robotic Object-Centered Planning
MDPI Robotics, 2025
The article “Agentic Workflows for Improving Large Language Model Reasoning in Robotic Object-Centered Planning”, coauthored with José-Luis Matez-Bandera, José-Raul Ruiz-Sarmiento, and Javier González-Jiménez, explores how LLMs can guide robots to identify the most relevant objects in a 3D environment represented by semantic maps.
To reduce LLM hallucinations and enhance reasoning, the study introduces three agentic workflows—Self-Reflection, Multi-Agent Reflection, and LLM Ensemble—that iteratively review and refine the model’s responses.
Using semantic maps generated from the ScanNet and SceneNN datasets, experiments show that reflection-based workflows improve object retrieval accuracy by up to 10 % compared with the baseline system.
Awards
OMRON Award for Best Paper in the Computer Vision Thematic Group 2024
Jornadas de Automática (JJAA) 2024 — Málaga, Spain
I received the OMRON Award for Best Paper of the Computer Vision Thematic Group, which included a €300 prize, for the work “Modelos a gran escala para mapeo semántico en robótica móvil” co-authored with José-Raúl Ruiz-Sarmiento, José-Luis Matez-Bandera, and Javier González-Jiménez.
Award information available here.

Archive